Polio Outbreak
November 1, 2018
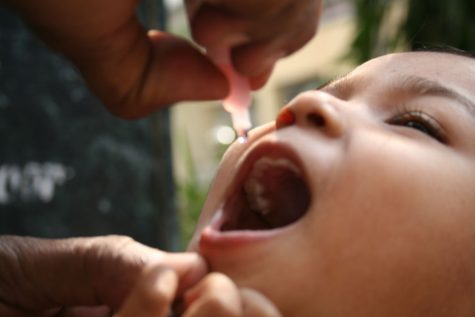
Polio, or poliomyelitis, is a crippling and potentially deadly infectious disease. It is caused by the polio virus. The virus spreads from person to person, and can invade an infected person’s brain and spinal cord, causing paralysis (the loss of the ability to move). Most people who get infected with polio virus (about 72 out of 100) will not have visible symptoms. About 1 out of 4 people with the polio virus infection will have flu-like symptoms such as a sore throat, fever, tiredness, nausea, headache, and stomach pain. These symptoms usually last two to five days and go away on their own. There are two types of vaccines that could potentially protect a person against this disease: the oral polio virus vaccine (OPV) and the inactivated polio virus vaccine (IPV). This vaccine is distributed through a injection in the leg or arm depending on the patient’s age. Today, only three countries in the world have not stopped the transmission of polio (Pakistan, Afghanistan and Nigeria). It can only take one person travelling from another country to bring the disease into the US then spread. Doctors strongly recommend talking to your doctor today about getting checked for Polio.